The path towards Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) for Department of Defense (DoD) contractors handling Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and Federal Contract Information (FCI) has been clearly defined by the CMMC-Accreditation Body (CMMC-AB):
- Comply with currently active DFARS 7012 standards – this includes SSPs and POAMs; the CMMC-AB will not accept POAMs for 3rd party certification.
- Determine the scope of your organizational IT systems to Identify all non-public facing FCI and CUI within scope – reference DoD Instruction 5200.48 for CUI guidance.
- Familiarize yourself with new CMMC terminology and begin CMMC Readiness exercises to prepare for eventual 3rd party certification – DoD contractors handling CUI will need to achieve a minimum of Level 3 CMMC certification, Levels 4 & 5 will be required on a very rare basis mainly for prime contractors.
Be sure to utilize the (draft) Glossary of terms posted on the CMMC-AB website while conducting your research. Learning these terms will simplify any future assessment and/or certification efforts.
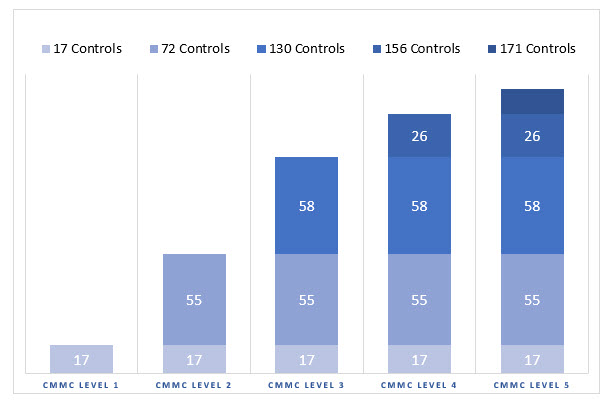
CMMC Level 2 (72 Controls): about half of NIST 800-171 controls
CMMC Level 3 (130 Controls): all 110 controls from NIST 800-171 plus 20 other controls
Defense Industrial Base (DIB) organizations that have accurately self-attested their compliance with the DFARS 7012 standard will have already implemented 110 of the 130 controls required to achieve CMMC Level 3 certification. The additional 20 controls (or GAP Controls) that must be implemented are:
AM.3.036. Define procedures for the handling of CUI data.
AU.3.048. Collect audit logs into a central repository.
AU.2.044. Review audit logs.
IR.2.093. Detect and report events.
IR.2.094. Analyze and triage events to support event resolution and incident declaration.
IR.2.096. Develop and implement responses to declared incidents according to pre-defined procedures.
IR.2.097. Perform root cause analysis on incidents to determine underlying causes.
RE.2.137. Regularly perform and test data back-ups.
RE.3.139. Regularly perform complete and comprehensive data back-ups and store them off-site and offline.
RM.3.144. Periodically perform risk assessments to identify and prioritize risks according to the defined risk categories, risk sources, and risk measurement criteria.
RM.3.146. Develop and implement risk mitigation plans.
RM.3.147. Manage non-vendor-supported products (e.g., end of life) separately and restrict as necessary to reduce risk.
CA.3.162. Employ code reviews of enterprise software developed for internal use to identify areas of concern that require additional improvements.
SA.3.169. Receive and respond to cyber threat intelligence from information sharing forums and sources and communicate to stakeholders.
SC.2.179. Use encrypted sessions for the management of network devices.
SC.3.192. Implement Domain Name System (DNS) filtering services.
SC.3.193. Implement a policy restricting the publication of CUI on publicly accessible websites (e.g., Forums, LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, etc.).
SI.3.218. Employ spam protection mechanisms at information system access entry and exit points.
SI.3.219. Implement DNS or asymmetric cryptography email protections.
SI.3.220. Utilize email sandboxing to detect or block potentially malicious email attachments.
Echoing the recommendation of the CMMC-AB, we strongly encourage DIB organizations begin conducting proactive CMMC Readiness exercises. Working with OCD Tech to assess your organization against the current (NIST 800-171) and future (CMMC) standards will bring you up to date with the existing requirements while simultaneously positioning your organization to successfully achieve CMMC certification.
Contact Us


